The VerticalLineAnnotation
The VerticalLineAnnotation draws the vertical line between Y1 and Y2 coordinates at X1:
Note
You might also be interested in learning about the HorizontalLineAnnotation since it's very similar with the Horizontal one.
Note
Examples of the Annotations usage can be found in the SciChart Android Examples Suite as well as on GitHub:
The VerticalLineAnnotation class is inherited from LineAnnotation, and hence, provides the stroke property which is used to define the line annotation color. It expects a PenStyle object. To learn more about Pens and Brushes and how to utilize them, please refer to the PenStyle, BrushStyle and FontStyle article.
Note
To learn more about Annotations in general - please see the Common Annotation Features article.
In general case, the position of an VerticalLineAnnotation can only be defined by the x1 value, which will lead to full-height vertical line at X1 coordinate.
Despite the above, it is possible to specify Y1 and Y2 coordinates for the line ends, but it will work differently while combined with different Gravity.
verticalGravity property can consume the following values:
- Gravity.TOP - the
Y1coordinate will be applied to the bottom end of a line. The line appears pinned to the top side. - Gravity.BOTTOM - the
Y1coordinate will be applied to the top end of a line. The line appears pinned to the bottom side. - Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL - both
Y1andY2coordinates will be applied. - Gravity.FILL_VERTICAL - both
Y1andY2coordinates are ignored. The line appears vertically stretched. This is the default value.
The Y1 and Y2 values can be accessed via the y1 and y2 properties.
Note
The xAxisId and yAxisId must be supplied if you have axis with non-default Axis Ids, e.g. in multi-axis scenario.
Create a VerticalLine Annotation
A VerticalLineAnnotation can be added onto a chart using the following code:
// Assume a surface has been created and configured somewhere
// Create a VerticalLine Annotation
final VerticalLineAnnotation verticalLine = new VerticalLineAnnotation(getContext());
// Allow to interact with the annotation in run-time
verticalLine.setIsEditable(true);
// In a multi-axis scenario, specify the XAxisId and YAxisId
verticalLine.setXAxisId("BottomAxisId");
verticalLine.setYAxisId("RightAxisId");
// Specify a desired position by setting coordinates and mode
verticalLine.setCoordinateMode(AnnotationCoordinateMode.RelativeX);
verticalLine.setY1(0.1);
// Specify the border color for the annotation
verticalLine.setStroke(new SolidPenStyle(0xFFFF1919, true, 2f, null));
// Add the annotation to the Annotations collection of the surface
surface.getAnnotations().add(verticalLine);
Note
To learn more about other Annotation Types, available out of the box in SciChart, please find the comprehensive list in the Annotation APIs article.
The AnnotationLabels collection
By default, the VerticalLineAnnotation does not show any labels. You can show a label by adding a AnnotationLabel to the annotationLabels collection, like below:
final AnnotationLabel annotationLabel = new AnnotationLabel(getContext());
annotationLabel.setText("Label text");
annotationLabel.setLabelPlacement(LabelPlacement.Axis);
verticalLine.annotationLabels.add(annotationLabel);
The Label position can be changed by setting the labelPlacement property which expects one of the LabelPlacement enumeration.
Note
Everything about AnnotationLabels collection and AnnotationLabel can be also applied to the HorizontalLineAnnotation
The AnnotationLabel Type
You can change appearance, position, custom value, etcetera for any annotation label which are listed below:
- setLabelStyle - applies style for AnnotationLabel.
- rotationAngle - allows to rotate annotation label text, expects degrees
- text - you can set custom text for your label.
- fontStyle - applies the FontStyle object onto the text.
Note
By default, AnnotationLabel uses its associated axis Y-value to display a label.
To learn more about Pens and Brushes and how to utilize them, please refer to the PenStyle, BrushStyle and FontStyle article.
Also, you can have more than one AnnotationLabel associated with HorizontalLineAnnotation by adding more than one to the annotationLabels collection.
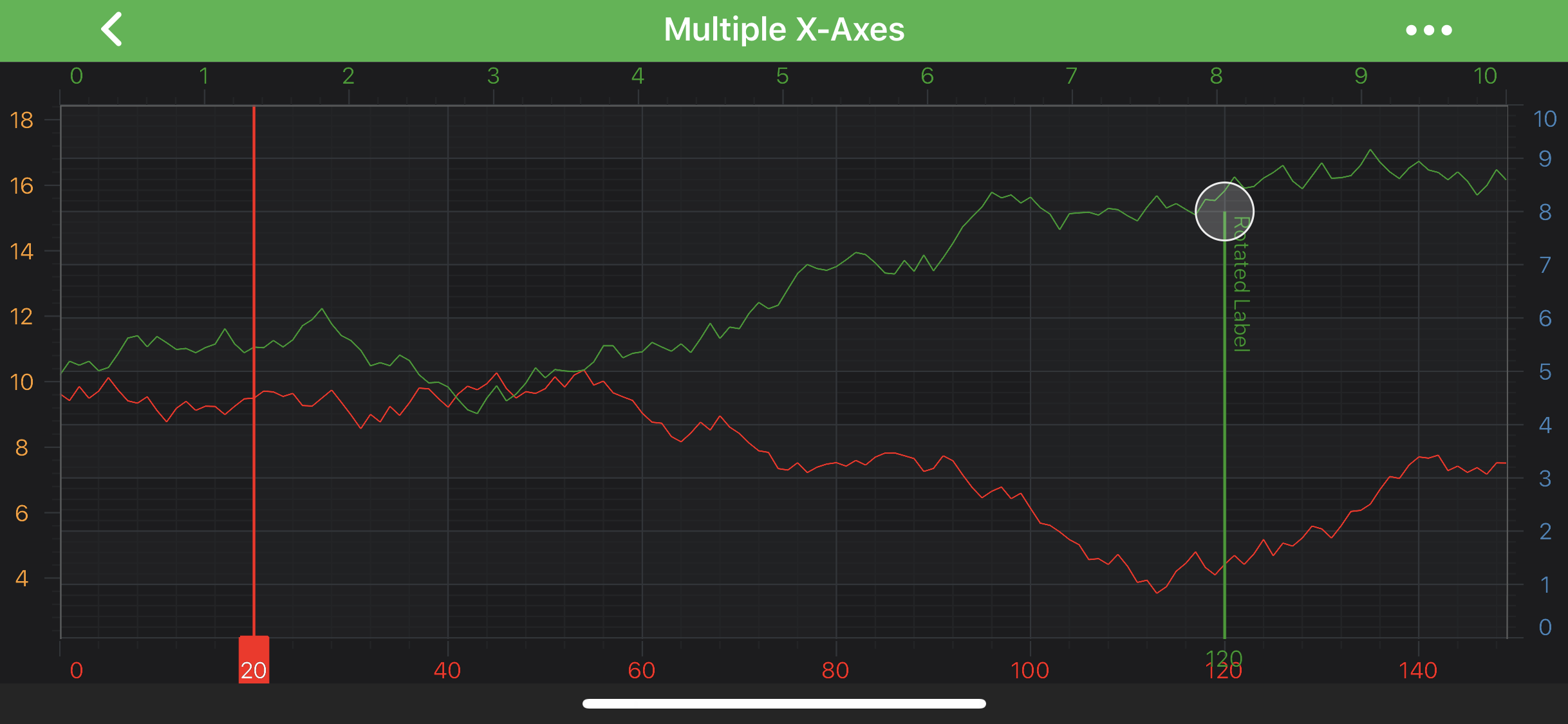
Please see the code below, which showcases the utilization of the above settings:
AnnotationLabel axisAnnotationLabel = new AnnotationLabel(getContext());
axisAnnotationLabel.setLabelPlacement(LabelPlacement.Axis);
axisAnnotationLabel.setPadding(0, 10, 0, 0);
AnnotationLabel annotationLabel = new AnnotationLabel(getContext());
annotationLabel.setLabelPlacement(LabelPlacement.TopRight);
annotationLabel.setText("Rotated Label");
annotationLabel.setRotationAngle(-90);
final VerticalLineAnnotation verticalLine = new VerticalLineAnnotation(getContext());
verticalLine.setY1(8);
verticalLine.setVerticalGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM);
Collections.addAll(verticalLine.annotationLabels, annotationLabel, axisAnnotationLabel);
This will result in the following:
Annotation Label Value and TextFormatting
By default, the label text is formatted by the textFormatting property. For more information, refer to the Axis Labels - TextFormatting and CursorTextFormatting article.
But you can also override the default behaviour by providing a custom IFormattedValueProvider for your VerticalLineAnnotation corresponding property.
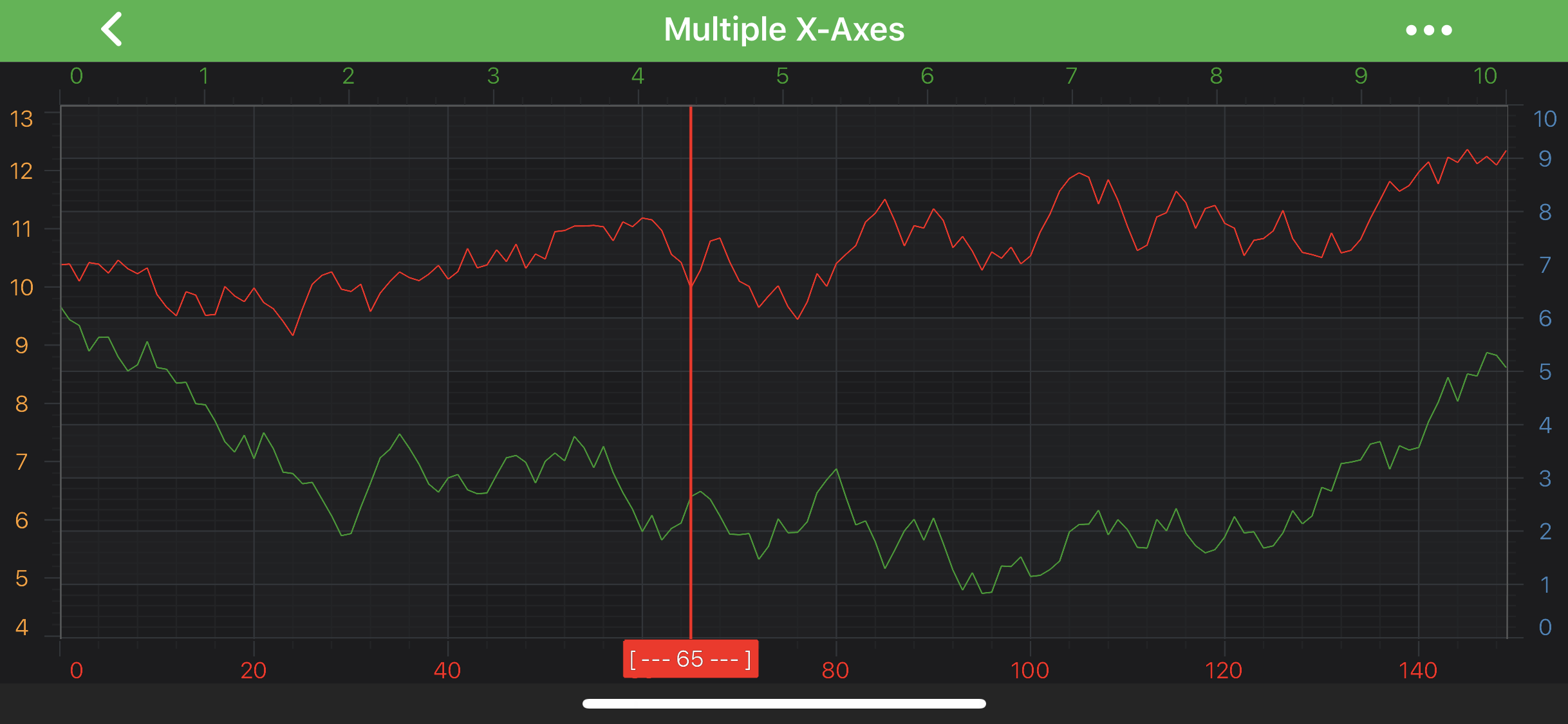
Let's see a short example which shows how to use the above:
class AnnotationValueProvider implements IFormattedValueProvider {
@Override
public CharSequence formatValue(AxisInfo axisInfo) {
return axisInfo != null ? String.format("[ --- %s --- ]", axisInfo.axisFormattedDataValue) : null;
}
}
final VerticalLineAnnotation verticalLine = new VerticalLineAnnotation(getContext());
verticalLine.setXAxisId("BottomAxisId");
verticalLine.setYAxisId("RightAxisId");
verticalLine.setX1(65);
verticalLine.setStroke(new SolidPenStyle(0xFFFF1919, true, 4f, null));
// Provide custom IFormattedValueProvider for the annotation
verticalLine.setFormattedLabelValueProvider(new AnnotationValueProvider());
AnnotationLabel axisAnnotationLabel = new AnnotationLabel(getContext());
axisAnnotationLabel.setLabelPlacement(LabelPlacement.Axis);
verticalLine.annotationLabels.add(axisAnnotationLabel);
This will result in the following:
Note
To learn more about other Annotation Types, available out of the box in SciChart, please find the comprehensive list in the Annotation APIs article.